
Series of Basic biology for life science-1.
What are differences between organisms and non-organisms?
Everything on earth are made of atoms and molecules. Oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen are the most important atoms for organisms. We are surrounded by non-organisms as well, like TVs, PCs, or cars etc. These non-organisms in our world where we live contains a lot of silicon mainly.
What our body is made of? Proteins are the most important component together with water, which are made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen mainly. Proteins are required for our essential activities like, vision, memory, and reproduction, etc.
Proteins are made of 20 different amino acids which are connected one by one and form a linear string. More than 100 thousand proteins we have are required as catalysts for many chemical reactions within our body. The amino acid sequence of each protein is unique. The sequences are not the same even among your brothers and sisters which contribute for your uniqueness and make diversity among individual human beings. The sequence information kept in DNA is derived from your parents, while the difference in the sequences of proteins among your brothers and sisters is created based on a special process during reproduction process. This mechanism has been equipped during biological evolution since the first cell on the earth was born 38 billion years ago. This diversity is very important in the sense of evolution. Without this diversity risks against the environmental changes on the earth surrounding us increase. If humans have a single set of sequences among brothers and sisters we could not have survived through the big environmental changes that happened on earth.
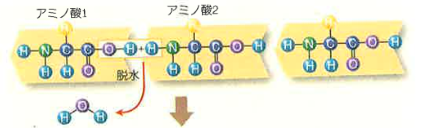

Based on the sequence information of amino acids in a protein, proteins are synthesized in a protein producing factory, named the ribosome. This protein synthesis mechanism is shared by all organisms. This common mechanism through all organisms is called “central dogma”. COVID19 also shares the central dogma and produces their daughter viruses which has RNA for the amino acid sequence information instead of DNA. COVID19 has genetic information as RNA but they do not have the protein synthesis factory. They have to use the factory of human cells. In this sense, COVID19 is not an organism because they can’t produce daughter viruses by themselves. In Fig. a life cycle of COVID19 is shown. To produce daughter viruses, they need to synthesize RNA at first by using a RNA replicating enzyme. If we can inhibit the function of this enzyme through the use of a drug, we can stop the growth of the virus. This type of drug is close to the final stage for our use. But, of course, vaccines against COVID are still powerful to stop viral growth.


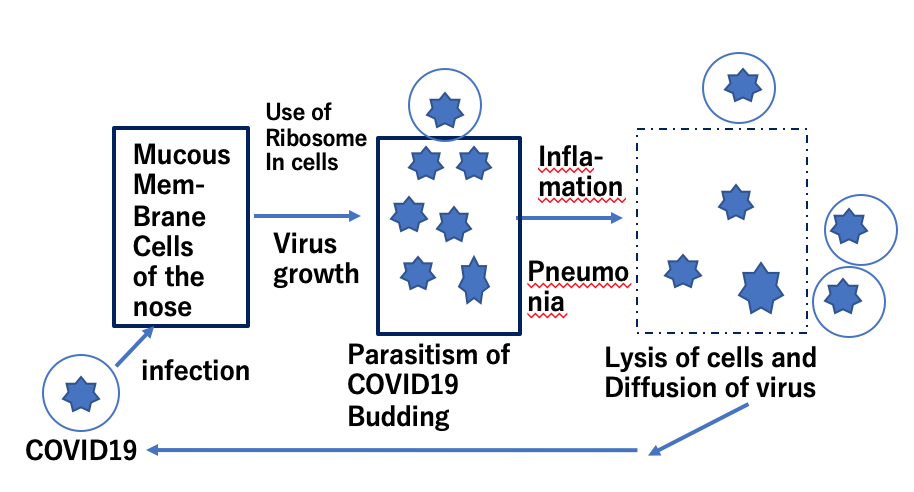
We cannot estimate the real number of all viruses on earth now. Virus can stay only in living cells including bacteria. This means new viruses may exist in most living organisms which we have not observed and they may infect humans someday. COVID19 is strongly thought to have originated in a bat and then infected humans. In our whole DNA (genome) the amino acid sequence information occupies only less than 10 percent. Functions of the majority of the genome are not necessarily clear yet but some of them look similar to virus DNA. This finding suggests that these virus-like structures in genome DNA might be traces of viral infection during evolution and that we need to prepare for another attack of a new virus.
